For individuals with limited mobility, a wheelchair can offer essential support, allowing them to maintain independence and improve their quality of life. A wheelchair may be considered medically necessary when an individual’s mobility is significantly impaired due to a medical condition or disability. In many cases, a healthcare provider must evaluate the severity of the condition and its impact on the individual’s ability to perform daily activities. Below, we will explore the diagnoses that typically warrant the use of a wheelchair and explain how mobility aids can improve the lives of those with mobility limitations.
1. Spinal Cord Injuries
Spinal cord injuries, often resulting from accidents, trauma, or degenerative conditions, can cause partial or total paralysis, significantly impacting an individual’s ability to walk. Depending on the location and severity of the injury, a wheelchair may be essential for moving around. Conditions like paraplegia (paralysis of the lower body) or quadriplegia (paralysis of both the upper and lower body) often result in the need for a wheelchair to provide mobility and independence.
2. Neurological Disorders
Several neurological conditions affect the brain or nerves, leading to muscle weakness, coordination issues, and loss of movement. These disorders may require the use of a wheelchair, including:
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): MS is a progressive disease that can impair movement, cause muscle spasms, and reduce balance, making a wheelchair essential for mobility.
- Parkinson’s Disease: This progressive disorder can lead to tremors, slow movements, and balance issues, which may eventually make walking difficult and a wheelchair necessary.
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS): ALS, also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, causes muscle weakness and paralysis, often making a wheelchair essential as the condition advances.
- Cerebral Palsy: A group of disorders that affect muscle tone, movement, and motor skills, cerebral palsy may lead to significant mobility challenges, requiring a wheelchair for daily activities.
- Stroke: A stroke can result in partial paralysis or weakness on one side of the body, limiting an individual’s ability to walk and making a wheelchair necessary.
3. Musculoskeletal Conditions
Certain musculoskeletal conditions can severely limit a person’s ability to walk, making a wheelchair necessary. These conditions include:
- Osteoarthritis: Severe arthritis can result in joint pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion in the legs, making it difficult or painful to walk.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: This autoimmune condition can cause inflammation and damage to the joints, impairing mobility and potentially requiring a wheelchair for assistance.
- Muscular Dystrophy: This genetic disorder causes muscle weakness and loss of muscle mass, leading to difficulty walking and eventually necessitating the use of a wheelchair.
- Hip or Knee Replacements: Individuals who have had hip or knee replacement surgeries, especially those with complications or who experience pain and instability, may need a wheelchair temporarily or permanently.
4. Amputations
People who have lost one or more limbs due to traumatic injury, disease, or surgery often require a wheelchair for mobility. In cases where prosthetic limbs are not a viable option or provide insufficient support, a wheelchair offers a stable and reliable means of movement. Additionally, amputees may use wheelchairs to reduce strain on their remaining limbs during the rehabilitation process.
5. Chronic Conditions and Fatigue Disorders
Chronic conditions that cause fatigue or weakness can impair an individual’s ability to walk long distances or maintain balance. Some examples include:
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS): Individuals with CFS experience extreme fatigue, muscle weakness, and difficulties with physical exertion, often leading to the need for a wheelchair to conserve energy.
- Heart Disease: Severe cardiovascular conditions can cause fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath, which may limit the ability to walk or stand for prolonged periods, making a wheelchair helpful for mobility.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): COPD causes difficulty breathing and can lead to fatigue, making it harder for individuals to walk long distances, requiring the use of a wheelchair.
6. Balance Disorders
Conditions that affect balance and coordination, such as vestibular disorders or vertigo, can make it difficult for an individual to walk without the risk of falling. A wheelchair may be prescribed to prevent injury and improve safety while providing greater mobility and independence.
7. Severe Obesity
In some cases, severe obesity can cause joint pain, muscle weakness, and fatigue, which makes it difficult or painful to walk. For individuals who experience extreme weight-related mobility limitations, a wheelchair can assist in performing daily tasks and preventing further health complications.
8. Other Conditions
Other diagnoses that may necessitate the use of a wheelchair include:
- Gait Disorders: Conditions like ataxia, where there is difficulty coordinating muscle movements, can make walking extremely challenging.
- Severe Deformities or Limb Defects: Individuals with severe limb deformities, either congenital or acquired, may require a wheelchair if they cannot walk or have limited walking ability.
- Injuries or Surgeries: After severe accidents, surgeries, or fractures, individuals may require a wheelchair temporarily during recovery if walking is not possible due to injury or post-surgical restrictions.
9. Assessment and Prescription
The process of determining if a wheelchair is necessary typically begins with a medical assessment by a healthcare professional, such as a physician, physical therapist, or occupational therapist. The assessment will focus on the individual’s specific diagnosis, their functional mobility limitations, and the impact the condition has on daily living. Depending on the diagnosis, the healthcare provider may recommend a wheelchair as part of the treatment plan.
Conclusion
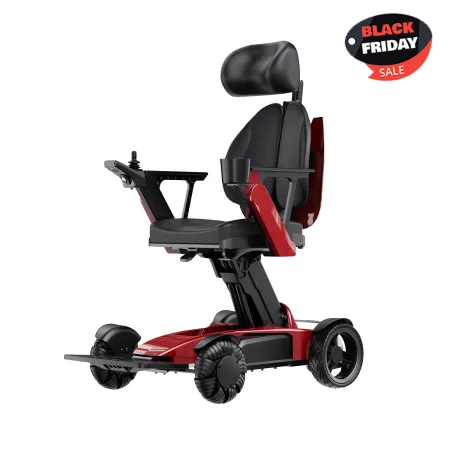
If you or a loved one is struggling with mobility issues due to a medical condition, a wheelchair may be an essential part of your treatment plan. Conditions such as spinal cord injuries, neurological disorders, musculoskeletal diseases, amputations, and chronic fatigue can all lead to the need for a wheelchair. Healthcare providers will assess your specific condition and determine whether a wheelchair is necessary. If you’re in need of a high-quality, reliable electric wheelchair, EASWE’s A10 and B10 models offer superior comfort, durability, and ease of use to support your mobility needs.